The Science of Spontaneous Purchases
Have you ever found yourself wandering through a store, only to walk out with items you never intended to buy? Whether it’s a shiny new gadget or a trendy piece of clothing, spontaneous purchases are a common occurrence for many consumers. But what exactly drives these impulsive buying decisions?
Unlocking the mind and exploring the psychology behind casual buying decisions can reveal some interesting insights into why we make these spontaneous purchases. Understanding the science behind these decisions can help us better comprehend our shopping habits and make more informed choices in the future.
One of the key factors that contribute to spontaneous purchases is the concept of instant gratification. When we see something that catches our eye and sparks our interest, our brain releases dopamine, the feel-good neurotransmitter. This surge of dopamine can create a sense of excitement and pleasure, making us more likely to make impulse purchases in the moment.
In addition to instant gratification, another psychological factor that plays a role in spontaneous purchases is the fear of missing out, also known as FOMO. When we see limited-time offers or exclusive deals, our brains can interpret these as opportunities that we don’t want to pass up. This fear of missing out can drive us to make quick decisions to ensure that we don’t regret not taking advantage of the opportunity.
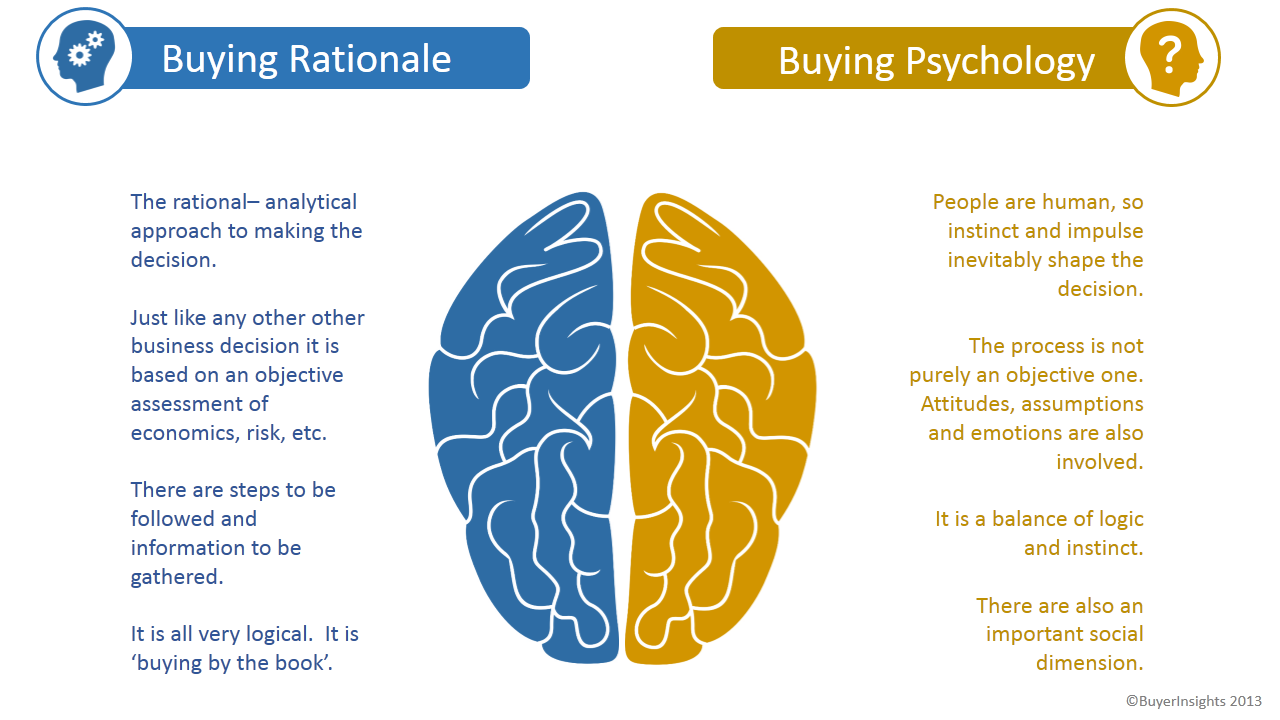
Image Source: sellerinsights.com
Furthermore, the power of emotional triggers can also influence our impulsive buying decisions. Marketers often use emotional appeals in their advertising to evoke specific feelings in consumers, such as happiness, nostalgia, or excitement. These emotional triggers can create a strong connection between the product and the consumer, leading to impulsive purchases driven by our emotions.
Another interesting aspect of spontaneous purchases is the role of social influence. In today’s digital age, social media plays a significant role in shaping our buying decisions. When we see influencers or friends endorsing a product, we may feel pressured to make a purchase in order to fit in or keep up with the latest trends. This social influence can greatly impact our impulsive buying behavior.
Moreover, the concept of cognitive biases can also contribute to spontaneous purchases. Our brains are wired to take mental shortcuts and make quick decisions based on limited information. This can lead us to overlook potential drawbacks or rationalize our impulsive purchases in order to justify our decisions. By understanding these cognitive biases, we can become more aware of our thought processes and make more mindful buying choices.
In conclusion, the science of spontaneous purchases is a fascinating field that delves into the intricacies of the consumer mind. By unlocking the psychology behind casual buying decisions, we can gain valuable insights into our shopping habits and behaviors. From the allure of instant gratification to the power of emotional triggers and social influence, there are numerous factors at play that drive impulsive buying decisions. By being aware of these psychological factors, we can make more informed choices and navigate the world of consumerism with a better understanding of our own minds.
Delving into the Whims of the Consumer Mind
Have you ever found yourself standing in front of a display of shiny new gadgets, feeling an irresistible urge to make a purchase? Or perhaps you’ve been browsing through a clothing store and suddenly feel drawn to a particular item, even though you didn’t plan on buying anything that day. These moments of impulse buying are not uncommon, and they often leave us wondering why we make these spontaneous decisions.
The psychology behind casual buying decisions is a fascinating subject that delves into the whims of the consumer mind. It goes beyond simple desire or need and taps into our emotions, preferences, and even our subconscious. Understanding the factors that influence these decisions can shed light on why we sometimes make purchases on a whim.
One of the key factors that play a role in casual buying decisions is emotional appeal. Many products are designed to evoke certain emotions in consumers, whether it’s a sense of excitement, nostalgia, or even security. Marketers and advertisers understand the power of emotions in driving consumer behavior, which is why they often use emotional appeals in their campaigns.
For example, a commercial for a luxury car may emphasize the feeling of success and achievement that comes with owning such a vehicle. Seeing this ad could trigger feelings of aspiration and desire in consumers, leading them to make a spontaneous purchase. Similarly, a nostalgic packaging design for a snack food could evoke memories of childhood and create a sense of comfort and familiarity, prompting consumers to buy it on impulse.
Another factor that influences casual buying decisions is social influence. We are social creatures, and we often look to others for cues on what to buy and how to behave. This phenomenon is known as social proof, and it plays a significant role in our purchasing decisions. When we see others buying a particular product or endorsing a brand, we tend to follow suit, assuming that it must be a good choice.
Social media has amplified the power of social influence, with influencers and celebrities promoting products to their followers. The allure of celebrity endorsements can be strong, as consumers aspire to emulate their favorite stars. This can lead to impulsive purchases based on the desire to be like the influencer or to be part of a certain lifestyle.
In addition to emotions and social influence, cognitive biases also play a role in casual buying decisions. Our brains are wired to take mental shortcuts and make quick decisions, which can sometimes lead to errors in judgment. For example, the scarcity effect causes us to place a higher value on items that are limited in quantity, leading us to make impulse purchases for fear of missing out.
Similarly, the anchoring effect occurs when we rely too heavily on the first piece of information we receive, such as a high initial price or a persuasive sales pitch. This can influence our perception of value and lead us to make purchases without fully considering all the options. By understanding these cognitive biases, marketers can tailor their strategies to exploit them and encourage impulsive buying behavior.
In conclusion, delving into the whims of the consumer mind reveals a complex interplay of emotions, social influence, and cognitive biases that drive casual buying decisions. By understanding these factors, marketers can create compelling campaigns that tap into consumers’ desires and motivations, ultimately leading to more successful sales. So the next time you find yourself making a spontaneous purchase, take a moment to consider the psychology behind it – you may just uncover the hidden forces at play in your mind.
Understanding the Psychology of Buying Decisions